Transport across biological membrane pdf
Online Reviews Of Physiology Biochemistry And Pharmacology: Special Issue On Water Transport Across Biological Membranes 2000. Online Reviews Of Physiology Biochemistry And Pharmacology: Special Issue On Water Transport Across Biological Membranes 2000 by Wilfred 4.4. TV Political Advertising in Italy: When products present other. The SAGE Handbook of Political Advertising. The …
15/11/2015 · A vital class of membrane proteins are those involved in active or passive transport of materials across the cell membrane or other subcellular membranes surrounding organelles. For a cell or an organism to survive, it is crucial that the right substances enter cells (e.g. nutrients) and the right substances are transported out of them (e.g. toxins).
potential gradient across a biological membrane. Active transport: The movement of molecules across a biological membrane against a concentration gradient using energy. Link The structure of phospholipids is discussed in Unit 1: Biochemistry of macromolecules and metabolic pathways. 4 Unit 14 Cell biology 14.2 iological cell membranes 3 Interdependence of organelles Protein sorting Protein
Biological Membranes Biology with Vernier 9 – 3 7. Rinse the beet pieces twice using a small amount of water. Immediately drain off the water. This will wash off …
A selection of multiple choice and missing word questions about cell membrane structure and the movement of substances across it.
Movement Across Biological Membranes Answers Membrane Fluidity For each of the following situations, choose if the membrane will be more or less fluid: 1. More double bonds in the fatty acid tails of phospholipids MORE 2. Longer fatty acid tails of phospholipids LESS 3. Phospholipids with unsaturated fatty acid tails MORE 4. Higher temperature MORE Transport mechanisms Given the …
Biological Membranes 12 MCB 110 – Spring 2008 – Nogales IV Membrane Fluidity IV A – Definition and Function • Fluidity is defined as “easy of flow” and is opposed to viscosity (resistance to flow).
In primary active transport the movement of a solute across the cell membrane is directly coupled to an energy-transducing chemical reaction, such as the coupling of sodium transport via the Na+
transport across cell membrane pdf The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside
Ion transport across biological membranes is a fundamental phenomenon ubiquitous in nature. Photosynthesis, the respiratory chain, ATP production, muscle contraction, neuronal signaling, and many other key biological processes depend on it.
2. Describe the kinetics of movement by active transport. E. Which forms of movement across the cell membrane can act against a concentration gradient;
Biological membranes• Membranes separate cells and organelles • Membranes consist of mainly lipid bilayers and Scribd is the world’s largest social reading and publishing site. Search Search
Biological membranes.pdf Biological Membrane es.scribd.com

(PDF) Transport Across Natural and Modified Biological
Human Physiology Transport System Rigorous Test Biological Membrane Kinetic Constant These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
Inorganic ions: low permeability across membrane, but can diffuse passively through cell membranes at rapid rates due to ion channels. Ion channels allow only passive transport across membranes.
A general quantum-mechanical description of molecular transport across biological membranes has been developed. The one-dimensional Schrödinger equation for the motion of ions and molecules across the biological membrane has been solved using reasonable potential barriers.
The transport of substances across the cell membrane is complex because the main physiological role of the membrane is the control of the substances that would enter or exit the cells. Life would
Transport in Biological Media is a solid resource of mathematical models for researchers across a broad range of scientific and engineering problems such as the effects of drug delivery, chemotherapy, or insulin intake to interpret transport experiments in areas of cutting edge biological research.

Download biological membranes or read online books in PDF, EPUB, Tuebl, and Mobi Format. Click Download or Read Online button to get biological membranes book now. This site is like a library, Use search box in the widget to get ebook that you want.
Membrane Channels. The definition of a channel (or a pore) is that of a protein structure that facilitates the translocation of molecules or ions across the membrane through the creation of a central aqueous channel in the protein.
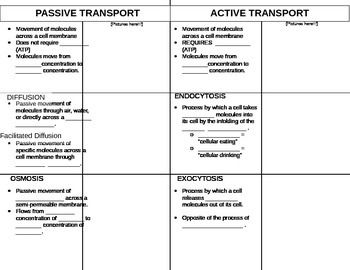
The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane is called passive transport because the cell does not have to expend energy to make it happen. The concentration gradient itself represents potential energy and drives diffusion. However, membranes are selectively permeable and therefore have different effects on the rates of diffusion of various molecules. In the case of water
and serve for transport of bigger molecules, which would not be otherwise able to pass across the bilayer [6]. We have started studies on transportation of hazardous (heavy) metals across the cytoplasmic membrane.
This second Volume in the series on Membrane Transport in Biology contains a group of essays on transport across single biological membranes separating the inside and outside of cells or organelles. We have not attempted to include material on all types of plasma and intracellular membranes, but rather have emphasized structures which have been studied relatively thoroughly. Four chapters
Diffusion Across Biological Membranes: a Simulation. Diffusion across Biological Membranes: A simulation Introduction Diffusion is the process by which collisions between molecules cause to …
Biological membranes• Membranes separate cells and organelles • Membranes consist of mainly lipid bilayers and
This book elucidates the mechanisms involved in biological membrane functions. It describes the new modalities and characterization for basic in vitro as well as computer models of biological membranes. Biological membranes are analyzed in terms of advances in molecular dynamics. The individual
Antibiotic assisted molecular ion transport across a membrane in real time Jian Liu, Xiaoming Shang, Rebecca Pompano and Kenneth B. Eisenthal* Department of Chemistry, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 USA.
There are many ways solutes are transported across the thin (~40 Å) hydrophobic barrier. Transport is divided into passive diffusion and active transport. A biological membrane is semi-permeable, being permeable to some molecules, most notably water, while being very impermeable to most solutes that require some form of transporter. Passive diffusion (simple and facilitated) only requires the
Antibiotic assisted molecular ion transport across a
Summary. This paper presents several equations derived from an asymmetrical nonconcentrative carrier mechanism for biological transport. These equations inter-relate the kinetic constants derived from different types of kinetic experiments, and act as criteria for the validity of the mechanism.
Passive transport of water across biological membranes also occurs through water channels. These are tiny pores formed by proteins called aquaporins . There are a variety of aquaporins and they are present on virtually every cell membrane.
Methods and compositions for transporting drugs and macromolecules across biological membranes are disclosed. In one embodiment, the invention includes a method for enhancing transport of a selected compound across a biological membrane, wherein a biological membrane is contacted with a … – is osmosis an example of active or passive transport Ion Transport Through Cell Membrane Channels Jan Gomułkiewicz 1, fundamental phenomenon is a transport of ions through cell membranes which ensures that the ion content of a cell is different from the one outside the cell. Cell membranes, due to their structure and a chemical composition (a two-lipid layer with immersed molecules of integral proteins) are characterized by a very low
T. Pomorski et al. Figure 1. Lipids can cross biological membranes by vari-ous mechanisms. Spontaneous diffusion refers to the non-specific lipid movement occurring between the membrane
Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane. A concentration gradient is a just a region of space over which the concentration of a substance changes, and substances will naturally move down their gradients, from an area of higher to an area of lower concentration.
across biological membrane is dependent on specific Integral Membrane Proteins called Uni-porters; Briefly describe the two types of passive transport across membranes. 8. Briefly describe active transport across the membranes, 9. Draw the general structure of Phospholipid, 10. List the common features of the models of membran transport systems 38. Title: Slide 1 Author: Valued Acer
As a molecular environment, the biological membrane with its lipid core, its integral and peripheral proteins, and its carbohydrate scaffolding is deceptively simple in overall plan but chaotically complex in its detailed organization and dynamics. That chemists are inspired by membranes and transport across the membrane barrier is hardly surprising.
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space) which protects the cell from its environment consisting of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
A vital class of membrane proteins are those involved in active or passive transport of materials across the cell membrane or other subcellular membranes surrounding organelles. For a cell or an organism to survive, it is crucial that the right substances enter cells (e.g. nutrients) and the right substances are transported out of them (e.g. toxins).
Biological membranes • Separate different compartments in the cell • Are dynamic and fluid structures • Consist of lipids and proteins.
Because much of what happens in a cell or in a virus occurs on, in, or across biological membranes, the study of membranes has rapidly permeated the fields of biology, pharmaceutical chemistry, and materials science. The Structure of Biological Membranes, Third Edition provides readers with an understanding of membrane structure and function that is rooted in the history of the field and
Biological Membrane & Transport Table of contents Membrane character molecular constituent of membrane supramolecular architecture of membrane membrane motion membrane protein peripheral protein integral protein types of integral protein topology of integral protein cell-cell interaction & adhesion membrane fusion passive transport erythrocyte’ s glucose transporter cotransport systems
transport, directly uses energy to transport molecules across a membrane. Example:Sodium-potassium pump, which helps to maintain the cell potential. Figure 7: Primary active transport.The action of the sodium -potassium pump is an example of primary active transport.
1. MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND MEMBRANE TRANSPORT IN PLANTS CELL The basic functional units of plants, as with all living organisms, is the cell. Indeed, the
As Level Cell Membrane Test ProProfs Quiz
Movement across membranes is included in first-level biology courses such as AS Biology. The main types of movement across membranes are simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport and Bulk Transport (including exocytosis and endocytosis). It is sometimes described as types of transport through cell membranes. Knowledge
Brings together different facets of membrane research in a universally understandable manner Emphasis on the historical development of the field Topics include membrane sugars, membrane models, membrane isolation methods, and membrane transport.
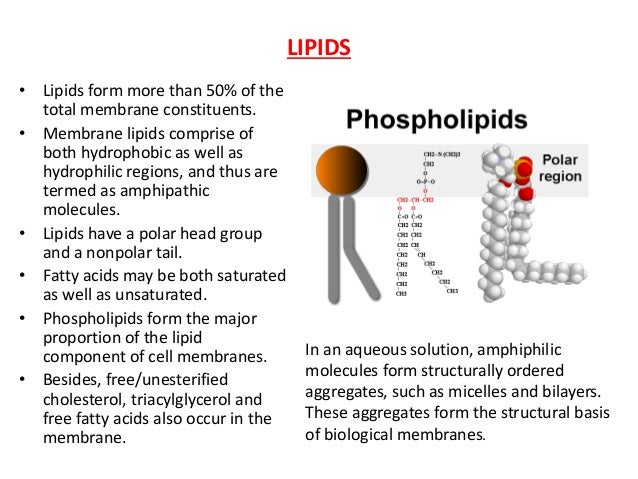
Before studying the passage of drugs across membranes it is necessary to recall the composition and structure of the membrane. Composition and structure of membranes Plasma membrane which surrounds each cell consists of approximately 60% of phospholipids and 40% of protein.
The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the extracellular environment. Its permeability properties ensure that essential molecules such as glucose, amino acids, and lipids readily enter the cell, metabolic intermediates remain in …
Artif Life Robotics (1998) 2:33-40 9 ISAROB 1998 Hirohumi Hirayama 9 Yoshimitsu Okita 9 Yuzo Fukuyama Optimal control of active transport across a biological membrane
In this article we will discuss about the Transport of Ions and Other Molecules through Biological Cell Membrane. The living organisms can be resolved into organs, glands, tissues, cells and organelles.
Calcium also plays important roles in regulating cell-membrane permeability, in ion and hormone transport, and in a range of enzyme functions. Along with potassium, calcium helps detoxify organic acids in cell vacuoles by inducing their precipitation. Calcium is primarily translocated via the xylem.
Apart from some passive transport mechanisms, all membrane proteins function in a directed way, and their correct insertion in the cell membrane is essential for their biological function.
the biochemical society biological membranes biochemistry across the school curriculum guidance notes for advanced biology no. 8 founded 1911 t h e • b io
Transport Across Natural and Modi˚ ed Biological Membranes

COMPOSITION AND METHOD FOR ENHANCING TRANSPORT ACROSS
Biological Membranes 1. Which of the following statements about passive and primary active transport proteins is FALSE? A. They are both integral membrane proteins. B. They both show a high degree of selectivity. C. Both require a concentration gradient to function. D. They both change conformation during transport. 2. Which one of the following statements is TRUE for passive transport across
transport across the endothelium and is an important factor in the interaction between blood- borne cells and the endothelium. Studies have demonstrated that the glycocalyx in a capillary is
Diagrammatic representation of the various mechanisms for the passage/transport of ions and molecules across biological membranes. The action of transporters is divided into two classifications: passive-mediated transport (also called facilitated diffusion) and active transport.
Cell Membranes • Consist predominantly of phospholipids and protein • Phospholipid bilayer (esp. hydrocarbon tails) limits ability of some substances to enter/leave the cell – Inhibits movement of larger and/or more hydrophilic solutes • Selectively permeable Cell Membranes • Membrane proteins provide alternate routes for movement • Highly specific in what substances are
on natural and modified biological membranes, transport across the membrane bar- rier, and methodology associated with membrane feature modulation and finally their analysis.
Ion transport across biological membranes and its control Workshop organized by the Sonderforschungsbereich 160 – Eigenschaften biologischer Membranen – September 25-27 1983, Maria Laach, FRG B. Deuticke, E. Hildebrand, J. Schnakenberg and H. Stieve Sonderforschungsbereich 160, R WTH Au&en, Templergraben 55, D-5100 Aachen, FRG Received 16 July 1984 It was the aim of …
Cell Membrane Permeability an overview ScienceDirect
09 Biological Membranes Vernier Software & Technology
Among the pathways for protein translocation across biological membranes, the ΔpH-dependent/Tat system is unusual in its sole reliance upon the transmembrane pH gradient to drive protein transport.
• Fluid&mosaics&of&lipids&and&proteins • Phospholipids&5abundant Phospholipids&are&hipathic&molecules&(has&hydrophobic&and& hydrophilic&end) • The&fluid
Energetics of Protein Transport across Biological Membranes


Biological cell membranes contentextra.com
Passive Transport an overview ScienceDirect Topics
– Membrane Structure and Function s3.studentvip.com.au
Biological Membranes Amazon Simple Storage Service


Movement across membranes AS Biology – IvyRose Holistic
Biological membranes.pdf Biological Membrane scribd.com
Passage of drugs across membranes Pharmacorama
Biological cell membranes contentextra.com
Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane. A concentration gradient is a just a region of space over which the concentration of a substance changes, and substances will naturally move down their gradients, from an area of higher to an area of lower concentration.
In this article we will discuss about the Transport of Ions and Other Molecules through Biological Cell Membrane. The living organisms can be resolved into organs, glands, tissues, cells and organelles.
Biological membranes• Membranes separate cells and organelles • Membranes consist of mainly lipid bilayers and Scribd is the world’s largest social reading and publishing site. Search Search
Human Physiology Transport System Rigorous Test Biological Membrane Kinetic Constant These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
and serve for transport of bigger molecules, which would not be otherwise able to pass across the bilayer [6]. We have started studies on transportation of hazardous (heavy) metals across the cytoplasmic membrane.
Biological cell membranes contentextra.com
Biological Membranes Amazon Simple Storage Service
In this article we will discuss about the Transport of Ions and Other Molecules through Biological Cell Membrane. The living organisms can be resolved into organs, glands, tissues, cells and organelles.
The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the extracellular environment. Its permeability properties ensure that essential molecules such as glucose, amino acids, and lipids readily enter the cell, metabolic intermediates remain in …
A selection of multiple choice and missing word questions about cell membrane structure and the movement of substances across it.
Summary. This paper presents several equations derived from an asymmetrical nonconcentrative carrier mechanism for biological transport. These equations inter-relate the kinetic constants derived from different types of kinetic experiments, and act as criteria for the validity of the mechanism.
Biological membranes • Separate different compartments in the cell • Are dynamic and fluid structures • Consist of lipids and proteins.
Transport Across Natural and Modi˚ ed Biological Membranes
Membrane Structure and Function s3.studentvip.com.au
transport across cell membrane pdf The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space) which protects the cell from its environment consisting of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
1. MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND MEMBRANE TRANSPORT IN PLANTS CELL The basic functional units of plants, as with all living organisms, is the cell. Indeed, the
Transport in Biological Media is a solid resource of mathematical models for researchers across a broad range of scientific and engineering problems such as the effects of drug delivery, chemotherapy, or insulin intake to interpret transport experiments in areas of cutting edge biological research.
This book elucidates the mechanisms involved in biological membrane functions. It describes the new modalities and characterization for basic in vitro as well as computer models of biological membranes. Biological membranes are analyzed in terms of advances in molecular dynamics. The individual
Biological Membrane & Transport Table of contents Membrane character molecular constituent of membrane supramolecular architecture of membrane membrane motion membrane protein peripheral protein integral protein types of integral protein topology of integral protein cell-cell interaction & adhesion membrane fusion passive transport erythrocyte’ s glucose transporter cotransport systems
Biological Membranes Download eBook PDF/EPUB
Chapter 2.1 Cell Membrane Mechanics and Adhesion
The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane is called passive transport because the cell does not have to expend energy to make it happen. The concentration gradient itself represents potential energy and drives diffusion. However, membranes are selectively permeable and therefore have different effects on the rates of diffusion of various molecules. In the case of water
This book elucidates the mechanisms involved in biological membrane functions. It describes the new modalities and characterization for basic in vitro as well as computer models of biological membranes. Biological membranes are analyzed in terms of advances in molecular dynamics. The individual
Transport in Biological Media is a solid resource of mathematical models for researchers across a broad range of scientific and engineering problems such as the effects of drug delivery, chemotherapy, or insulin intake to interpret transport experiments in areas of cutting edge biological research.
In primary active transport the movement of a solute across the cell membrane is directly coupled to an energy-transducing chemical reaction, such as the coupling of sodium transport via the Na
Biological Membrane & Transport Table of contents Membrane character molecular constituent of membrane supramolecular architecture of membrane membrane motion membrane protein peripheral protein integral protein types of integral protein topology of integral protein cell-cell interaction & adhesion membrane fusion passive transport erythrocyte’ s glucose transporter cotransport systems
A vital class of membrane proteins are those involved in active or passive transport of materials across the cell membrane or other subcellular membranes surrounding organelles. For a cell or an organism to survive, it is crucial that the right substances enter cells (e.g. nutrients) and the right substances are transported out of them (e.g. toxins).
Isolation and Characterization of Biological Membranes
Quantum-mechanical theory for transport across biological
Transport in Biological Media is a solid resource of mathematical models for researchers across a broad range of scientific and engineering problems such as the effects of drug delivery, chemotherapy, or insulin intake to interpret transport experiments in areas of cutting edge biological research.
Quantum-mechanical theory for transport across biological
Artif Life Robotics (1998) 2:33-40 9 ISAROB 1998 Hirohumi Hirayama 9 Yoshimitsu Okita 9 Yuzo Fukuyama Optimal control of active transport across a biological membrane
Quantum-mechanical theory for transport across biological
Study of Transport of Biologically Important Compounds in
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND MEMBRANE TRANSPORT IN
Artif Life Robotics (1998) 2:33-40 9 ISAROB 1998 Hirohumi Hirayama 9 Yoshimitsu Okita 9 Yuzo Fukuyama Optimal control of active transport across a biological membrane
Transport in Biological Media 1st Edition – Elsevier
• Fluid&mosaics&of&lipids&and&proteins • Phospholipids&5abundant Phospholipids&are&hipathic&molecules&(has&hydrophobic&and& hydrophilic&end) • The&fluid
Cell & Molecular Biology Homework #3 Movement Across