Inhibitors and uncouplers of electron transport chain pdf
18/11/2018 · Uncouplers can be defined as A substance that uncouples phosphorylation of ADP from electron transfer. Uncoupling agents are compounds which dissociate the synthesis of ATP from the transport of
SA Is an Uncoupler and an Inhibitor of Mitochondrial Electron Transport. The above results are in accordance with those of Xie and Chen who observed inhibition of whole-tobacco cell respiration by 0.5 m m SA and noted that intracellular ATP levels decreased.
• Electron transfer occurs through a series of protein electron carriers, the final acceptor being O 2 ; the pathway is called as the electron transport chain.
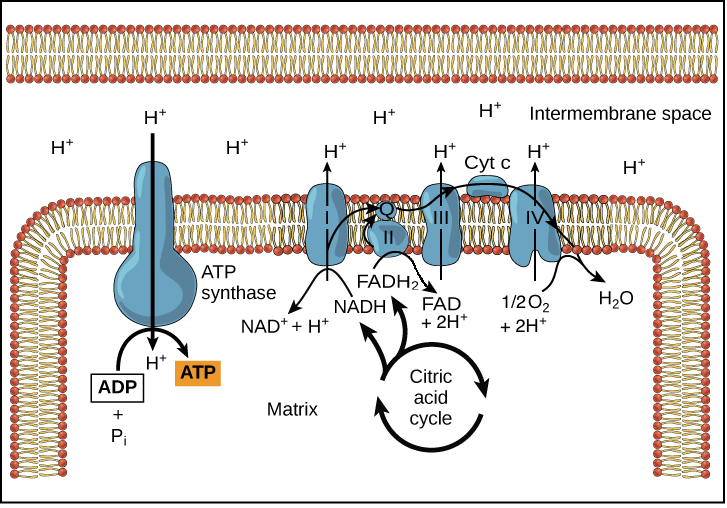
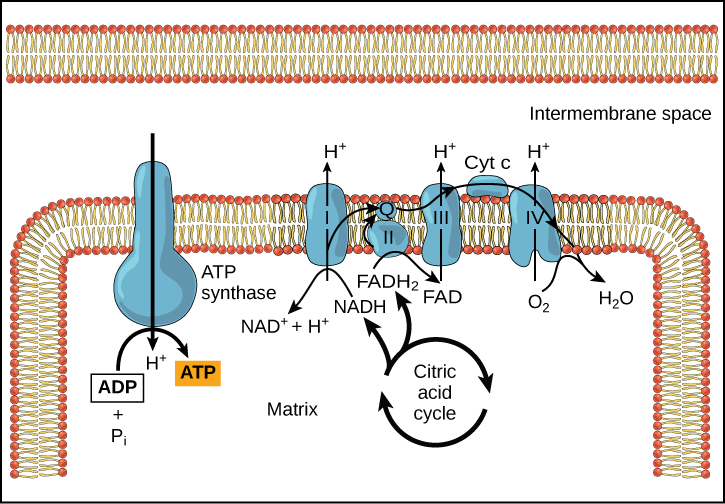
is called the electron transport chain (ETC), or the respiratory chain. The function of this process is to use the chemical energy released during the reoxidation of the carriers and the reduction of O 2, to make ATP from ADP and P i. The production of ATP driven by these redox reactions is called oxidative phosphorylation (sometimes OxPhos for short). The way this happens is a little cell
The electron transport chain carries both protons and electrons, passing electrons from donors to acceptors, and transporting protons across a membrane.
Answer to Question B-09 As described in a former post, the inhibitors of the Electron Transport Chain are substances that bind to some of the components of the ETC blocking its ability to change in a reversible form from an oxidized state to a reduced state.
However, this agent did not mimic HPV during normoxia, as may be expected for interference with the mitochondrial electron transport downstream in complex III. The uncouplers 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP, 10–200 μM) and carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone (FCCP, 1–3 μM) induced sustained vasoconstriction during normoxia, with enhancement of HPV by DNP at low and …
Uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria inhibit the coupling between the electron transport and phosphorylation reactions and thus inhibit ATP synthesis without affecting the respiratory chain and ATP synthase (H(+)-ATPase). Miscellaneous compounds are known to be uncouplers, but
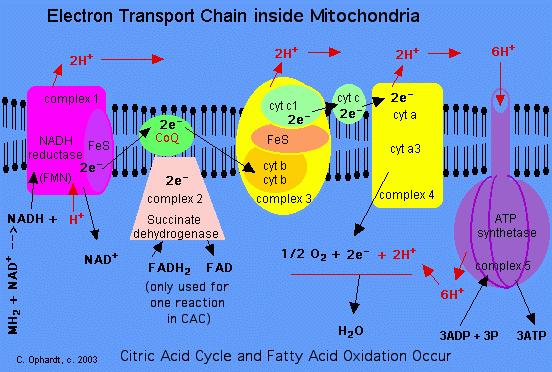
A) Site specific inhibitors -Specific inhibitors of electron transport chain are (figure-3) for example- 1) Inhibitors of complex I – Rotenone and amobarbital block electron transfer in NADH-Q oxidoreductase and thereby prevent the utilization of NADH as a substrate.
1) Respiratory chain inhibitors(e.g. cyanide, antimycin, rotenone & TTFA) block respiration in the presence of either ADP oruncouplers. 4) Transport inhibitors (e.g. atractyloside, bongkrekic acid, NEM) either prevent the export of ATP, or the import of raw …
Respiration inhibitors such as cyanide ions blocked the electron transport chain and were always effective in suppressing oxygen uptake, whereas phosphorylation inhibitors such as oligomycin, which prevented ATP manufacture, could only block respiration if the coupling were intact.
Inhibitors are the molecules which inhibit the electron transport chain, while the uncouplers are those molecules which uncouple/separates the complex I, II, III, and IV from the complex V (ATP synthase). Uncouplers have an important role to play in homeostasis. Many organisms possess the ability to
The biology of the mitochondrial electron transport chain is summarized. Our approach to the mechanism of uncouplers, inhibitors, and toxins is based on electron transfer (ET) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Extensive supporting evidence, which is broadly applicable, is cited. ROS can be
Evaluation of the electron transport chain inhibition and uncoupling of mitochondrial bioelectrocatalysis with antibiotics and nitro-based compounds
Inhibitors of electron transport chain: The make use of inhibitors gives much more information about the electron transport chain. They are categorized as . 1) Inhibitors of respiratory chain, 2) Inhibitors of oxidative phosphorylation, and 3) Uncouplers of phosphorylation. Inhibitors which arrest respiration are barbiturates such as amobarbital, antibiotic such as piericidin A, antimycin A
[starttext] Mitochondrial Respiratory or Electron transfer chain is located in inner mitochondrial membrane; Substrate are oxidized and e- released passes from Complex of low redox potential to higher redox potential, eventually being added to O2 at complex IV to form H 2 0
respiratory electron transport chain. •Oxidative Phosphorylation: NADH and QH 2 are oxidized by the respiratory electron transport chain (ETC). •ETC is set of membrane-embedded protein complexes that act as electron carriers, passing electrons from NADH and QH 2 to molecular oxygen. •As electrons move through the complexes, protons are transported across the inner mito. membrane …
Effects of Mitochondrial Inhibitors and Uncouplers on

(PDF) Biological Oxidation (Electron transport chain
The pesticide rotenone specifically inhibits electron transfer early in the chain with inhibition of proton transport beginning at site 1. Actimycin A inhibits electron transfer and proton pumping at site 2. Cyanide, hydrogen sulfide, and azide inhibit electron flow between the cytochrome oxidase complex and O2 preventing the generation of a proton gradient at site 3. Symptoms of toxicity from
Uncouplers break the connection between electron transport and phosphorylation Electron transport is a motor Phosphorylation is the transmission Uncouplers let you put the car in NEUTRAL 3. Table 2.
uncouplers such as SF6847 can uncouple in the nanomolar range, whereas the less efficient uncouplers such as penta- chlorophenol and2,4-dinitrophenol are effective only in the
Environmental Health PerspectivesVol. 87, pp. 213-218, 1990 Uncouplers of Oxidative Phosphorylation by Hiroshi Terada* Study abuot uncoupling agents in the respiratory chain …
See Figure 7.1 (The electron transport chain in photosynthesis and the sites of action of herbicides that interfere with electron transfer in this chain (Q = electron acceptor; PQ = plastoquinone; page 2).
Electron transport chain NADH and FADH 2 can donate electron pairs to a specialized set of proteins that act as an electron conduit to oxygen: the electron transport chain.
What is the difference between an inhibitor of electron transport and an uncoupler of electron transport with respect to NADH utilization, proton pumping, and ATP synthase? ETC Inhibitor: – NADH utilization: decreases because the ETC is fully reduced and cannot accept electrons
The effect of inhibitors on photosynthetic electron transport chain in canola leaf discs Emanuela Garbin Martinazzo1,2, various inhibitors on the photosynthetic electron transport chain using Chl a fluorescence in canola leaf discs. Material and methods Plant material and growth conditions Canola seeds were sown in pots with sand, and supplied with Hoagland solution. The plants were grown
The electron transport chain (ETC) is the major consumer of O2 in mammalian cells. The ETC passes electrons from NADH and FADH2 to protein complexes and mobile electron carriers. Coenzyme Q (CoQ) and cytochrome c (Cyt c) are mobile electron carriers in the ETC, and O2 is the final electron recipient. The malate and glycerol 3-P shuttles regenerate cytoplasmic NAD+

The significance of inhibitors and artificial electron acceptor and donor systems as experimental tools for studying the photosynthetic system is described by reviewing early classical articles. The historical development in unravelling the role and sequence of electron carriers and energy
a. inhibit one of the complexes in the electron transport chain. b. allow H + to leak into the mitochondrial matrix. c. inhibit ATP synthase. d. inhibit oxygen transport.
Inhibitors & Uncouplers February 24, 2003 Bryant Miles The electron transport chain was determined by studying the effects of particular inhibitors.
Inhibitors & Uncouplers February 24, 2003 Bryant Miles The electron transport chain was determined by studying the effects of particular inhibitors. Rotenone is a common insecticide that strongly inhibits the electron transport of complex I. Rotenone is a natural product obtained from the roots of several species of plants.
transport chain in the 1960s. Curious results were obtained. Curious results were obtained. They could reconstitute the electron transport chain in liposome vesicles.
Electron transport causes Complexes I, III, and IV to transport H + from the matrix (region of low [H + ] or high pH and negative electrical potential) across the inner
18/11/2008 · Answer to Question B-09 As described in a former post, the inhibitors of the Electron Transport Chain are substances that bind to some of the components of the ETC blocking its ability to change in a reversible form from an oxidized state to a reduced state.
Malonate is in fact a competitive inhibitor, and although we treat it as an inhibitor of electron transport it really is an enzyme inhibitor. Uncoupling agents Uncoupling is defined as a condition in which the rate of electron transport can no longer be regulated by an intact chemiosmotic gradient.
1 Oxidative Phosphorylation It means coupling of the electron transport in respiratory chain with phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP. It is a process by which …
The electron transport chain is shown here in abbreviated form. The circled numbers represent the various steps The circled numbers represent the various steps of the citric acid cycle.

Electron donation at site II, located on the linear portion of the electron transport chain between the two photosystems, has a higher affinity for reduced dichlorophenol-indophenol and precedes a phosphorylation site. The electron flow from this site is stimulated by uncouplers and inhibited by the quinone analogue.
58 Arch. MicrobioL, Vol. 120 (1979) work was undertaken to study the effects of inhibitors and uncouplers on tight-induced potential changes and
This video is about effects of certain inhibitors of electron transport chain on our energy metabolism. some of the inhibitors of electron transport chain mentioned here are rotenone, antimycin a, piericidin, amobarbital, cyanide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulphide, sodium azide, oligomycin.
Uncouplers and Inhibitors Much of our knowledge of mitochondrial function results from the study of toxic compounds. Specific inhibitors were used to distinguish the electron transport system from the phosphorylation system and helped to define the sequence of redox carriers along the respiratory chain.
The electron transport chain’s ultimate purpose is to create a proton gradient which is then used to drive ATP production. The mitochondrial outer membrane is porous, so the intermembrane space has the same ionic composition as the cytosol. The ETC creates a proton gradient across the inner membrane.
Solved Oxidative Phosphorylation Uncouplers A. Inhibit O
Start studying Inhibitors of the Electron Transport Chain. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
brief on Electron Transport Chain & Oxidative phosphorylation. various inhibitors and uncouplers affecting ETC and Oxidative phosphorylation Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising.
the electron transport chain, tricarboxylic acid cycle kinetics, mitochondrial calcium, sodium and proton handling, membrane ion transport processes that is coupled to oxidative phosphorylation, generation of ROS by complexes I
(e.g. electron transport inhibitors and uncouplers, various quinonoid compounds, etc.) the mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species can increase severalfold (2, 3).
Inhibitors of electron transfer and oxidative phosphorylation have proved to be useful tools to investigate the mechanisms of energy-yielding reactions in living cells, and therefore, in the study d~scfibed here we have investigated the effect of these inhibitors in T. cruzi on (a) respiration, (b) the redox level of its cytochromes, (c) substrate oxida- tion reactions and (d) growth – transport phenomena a unified approach solutions manual pdf Abstract. Uncouplers and inhibitors of electron transport affected growth and electron transport of rumen bacteria in various ways. Selenomonas ruminantium was not affected by inhibitor and uncoupler concentrations which affected growth and electron transport of Bacteroides ruminicola, B. succinogenes, and Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens.
Electron Transport Chain II The ETS is composed of four large protein complexes in the inner mitochndrial membrane and are involved in transferring electrons from reduced carriers (coenzymes) to …
• how various substrates, inhibitors, and uncouplers affect the rate of electron transport by monitoring changes in the rate of oxygen consumption; • how various electron donors affect P:O ratios.
The mitochondrial respiratory chain is known to form reactive oxygen species (ROS) by a mechanism strongly activated under resting (respiratory control or State 4) conditions when the electrochemical H + potential difference is high and the rate of electron transport is limited by discharge of .
The secondary metabolism products Reducing equivalents (NAHD and FADH 2) enter into the electron transport chain (ETC, Respiratory chain), where energy is released. This is called Tertiary metabolism (or) Internal Metabolism (or) Cellular Respiration.
A survey of the effect of inhibitors and uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation on chloroplast photophosphorylation led to the discovery of new inhibitors and uncouplers of this process. 2. n -Butyl-3,5-diiodo-4-hydroxybenzoate was found to inhibit both electron transport …
inhibitors such as cyanide; both block further electron transfer to oxygen. E) Uncouplers “short circuit” the proton gradient, thereby dissipating the proton motive force as heat.
E. Describe the use of Respiratory Inhibitors in elucidating the sequence of electron transport. IV. Describe how the energy released by the Electron Transport Chain is used.
6/10/2017 · This video is about effects of certain inhibitors of electron transport chain on our energy metabolism. some of the inhibitors of electron transport chain mentioned here are rotenone, antimycin a
Oxidative phosphorylation is the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) that accompanies the oxidation of NADH and other substrates by the mitochondrial electron transport chain
2 Prentice Hall c2002 Chapter 14 3 Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (1) Respiratory electron-transport chain (ETC) Series of enzyme complexes embedded in
Effect of oxidative phosphorylation uncoupler FCCP and F1F0-ATPase inhibitor oligomycin on the electromechanical activity of human myocardium 91
BioVision, Inc. BioVision, Inc., is a privately held Life Science company headquartered in the beautiful San Francisco Bay Area. BioVision develops and offers a wide variety of products including assay kits, antibodies, recombinant proteins & enzymes, and other innovative research tools for studying Apoptosis, Metabolism, Cell Proliferation
Mitochondrial inhibitors were chosen as being representative of established electron transport inhibitors and oxidative phosphorylation inhibitors and uncouplers of the classical mammalian respiratory chain.
Principles of Biochemistry “Oxidative Phosphorylation
The Mechanism of Uncoupling of Oxidative Phosphorylation by 2,4=Dinitrophenol* (Received for publication, January 18, 1967) electron transport particles by 2,4-dinitrophenol. Phosphorylating particles washed with 2,4-dinitrophenol lose coupling enzyme and with it the ability to form the energy-rich intermediate and to couple phosphorylation to electron transport. Phosphorylating particles
CHAPTER 20 OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION AND THE ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN . OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to describe the mitochondrion by drawing a cartoon of its membranes and noting the location of the TCA cycle, B-oxidation, the electron transport chain, the site of ATP synthase.
It has been reported that the oxidation of pyruvate by mitochondria immobilized on a bioanode can be used to power a biofuel cell, since the terminal electron acceptor, complex IV, of the electron transport chain is on the outer membrane of the mitochondria .
Electron Transport. Respiratory Chain, “Oxidative Phosphorylation” Purpose of the Pathway: convert NADH and FADH 2 into ATP The principle part of the chain consists of three complexes (I, III, IV) which are integral proteins of the inner mitochondrial membrane (not important to RBC’s…) and interact via mobile carriers of electrons.
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H + ions) across a membrane.
Inhibitors of electron transport chain mnemonic Inhibitors of electron transport chain mnemonic: Hi! In this post, we learn a mnemonic that tells us all about the inhibitors of the ETS! The mnemonic is, “CRAP Tightens Muscle AND Produces Muscle ACHe” Complex I inhibitors mnemonic. C – Chlorpromazine. R – Rotenone A – Amobarbital P – Piercidin A. Complex II inhibitors mnemonic. …
Electron transport chain in aerobically cultivated Zymomonas mobilis A single-nucleotide mutation in the −10 promoter region inactivates the narK2X promoter in Mycobacterium bovis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG and has an application in diagnosis
Evaluation of the electron transport chain inhibition and
Electron Transport Chain Inhibitors and Uncouplers
Inhibitors & Uncouplers biolympiads.com

Fatty acids as natural uncouplers preventing generation of
Inhibitors of the Electron Transport Chain Flashcards

Inhibitors in the functional dissection of the
Mitochondrial Uncouplers study Adenosine Triphosphate
– Electron transport chain Wikipedia
Mechanism of Mitochondrial Uncouplers Inhibitors and

Experiment CM-3 Mitochondrial Respiration iWorx
Some effects of uncouplers and inhibitors on growth and
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION AND THE ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
Nippostrongylus brasiliensis the effect of mitochondnal
Abstract. Uncouplers and inhibitors of electron transport affected growth and electron transport of rumen bacteria in various ways. Selenomonas ruminantium was not affected by inhibitor and uncoupler concentrations which affected growth and electron transport of Bacteroides ruminicola, B. succinogenes, and Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens.
The significance of inhibitors and artificial electron acceptor and donor systems as experimental tools for studying the photosynthetic system is described by reviewing early classical articles. The historical development in unravelling the role and sequence of electron carriers and energy
The pesticide rotenone specifically inhibits electron transfer early in the chain with inhibition of proton transport beginning at site 1. Actimycin A inhibits electron transfer and proton pumping at site 2. Cyanide, hydrogen sulfide, and azide inhibit electron flow between the cytochrome oxidase complex and O2 preventing the generation of a proton gradient at site 3. Symptoms of toxicity from
The mitochondrial respiratory chain is known to form reactive oxygen species (ROS) by a mechanism strongly activated under resting (respiratory control or State 4) conditions when the electrochemical H potential difference is high and the rate of electron transport is limited by discharge of .
• Electron transfer occurs through a series of protein electron carriers, the final acceptor being O 2 ; the pathway is called as the electron transport chain.
A) Site specific inhibitors -Specific inhibitors of electron transport chain are (figure-3) for example- 1) Inhibitors of complex I – Rotenone and amobarbital block electron transfer in NADH-Q oxidoreductase and thereby prevent the utilization of NADH as a substrate.
Electron transport causes Complexes I, III, and IV to transport H from the matrix (region of low [H ] or high pH and negative electrical potential) across the inner
A survey of the effect of inhibitors and uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation on chloroplast photophosphorylation led to the discovery of new inhibitors and uncouplers of this process. 2. n -Butyl-3,5-diiodo-4-hydroxybenzoate was found to inhibit both electron transport …
This video is about effects of certain inhibitors of electron transport chain on our energy metabolism. some of the inhibitors of electron transport chain mentioned here are rotenone, antimycin a, piericidin, amobarbital, cyanide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulphide, sodium azide, oligomycin.
Inhibitors in the functional dissection of the
The Oxidative Inactivation of Mitochondrial Electron
Oxidative phosphorylation is the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) that accompanies the oxidation of NADH and other substrates by the mitochondrial electron transport chain
1 Oxidative Phosphorylation It means coupling of the electron transport in respiratory chain with phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP. It is a process by which …
A) Site specific inhibitors -Specific inhibitors of electron transport chain are (figure-3) for example- 1) Inhibitors of complex I – Rotenone and amobarbital block electron transfer in NADH-Q oxidoreductase and thereby prevent the utilization of NADH as a substrate.
Abstract. Uncouplers and inhibitors of electron transport affected growth and electron transport of rumen bacteria in various ways. Selenomonas ruminantium was not affected by inhibitor and uncoupler concentrations which affected growth and electron transport of Bacteroides ruminicola, B. succinogenes, and Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens.
Experiment CM-3 Mitochondrial Respiration iWorx
Inhibitors & uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation & ETC
Uncouplers and Inhibitors Much of our knowledge of mitochondrial function results from the study of toxic compounds. Specific inhibitors were used to distinguish the electron transport system from the phosphorylation system and helped to define the sequence of redox carriers along the respiratory chain.
Malonate is in fact a competitive inhibitor, and although we treat it as an inhibitor of electron transport it really is an enzyme inhibitor. Uncoupling agents Uncoupling is defined as a condition in which the rate of electron transport can no longer be regulated by an intact chemiosmotic gradient.
Electron transport chain NADH and FADH 2 can donate electron pairs to a specialized set of proteins that act as an electron conduit to oxygen: the electron transport chain.
Respiration inhibitors such as cyanide ions blocked the electron transport chain and were always effective in suppressing oxygen uptake, whereas phosphorylation inhibitors such as oligomycin, which prevented ATP manufacture, could only block respiration if the coupling were intact.
The Mechanism of Uncoupling of Oxidative Phosphorylation by 2,4=Dinitrophenol* (Received for publication, January 18, 1967) electron transport particles by 2,4-dinitrophenol. Phosphorylating particles washed with 2,4-dinitrophenol lose coupling enzyme and with it the ability to form the energy-rich intermediate and to couple phosphorylation to electron transport. Phosphorylating particles
Inhibitors are the molecules which inhibit the electron transport chain, while the uncouplers are those molecules which uncouple/separates the complex I, II, III, and IV from the complex V (ATP synthase). Uncouplers have an important role to play in homeostasis. Many organisms possess the ability to
SA Is an Uncoupler and an Inhibitor of Mitochondrial Electron Transport. The above results are in accordance with those of Xie and Chen who observed inhibition of whole-tobacco cell respiration by 0.5 m m SA and noted that intracellular ATP levels decreased.
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H ions) across a membrane.
Electron Transport Chain Inhibitors and Uncouplers
Solved Oxidative Phosphorylation Uncouplers A. Inhibit O
a. inhibit one of the complexes in the electron transport chain. b. allow H to leak into the mitochondrial matrix. c. inhibit ATP synthase. d. inhibit oxygen transport.
Start studying Inhibitors of the Electron Transport Chain. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
2 Prentice Hall c2002 Chapter 14 3 Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (1) Respiratory electron-transport chain (ETC) Series of enzyme complexes embedded in
The electron transport chain (ETC) is the major consumer of O2 in mammalian cells. The ETC passes electrons from NADH and FADH2 to protein complexes and mobile electron carriers. Coenzyme Q (CoQ) and cytochrome c (Cyt c) are mobile electron carriers in the ETC, and O2 is the final electron recipient. The malate and glycerol 3-P shuttles regenerate cytoplasmic NAD
Mitochondrial inhibitors were chosen as being representative of established electron transport inhibitors and oxidative phosphorylation inhibitors and uncouplers of the classical mammalian respiratory chain.
Environmental Health PerspectivesVol. 87, pp. 213-218, 1990 Uncouplers of Oxidative Phosphorylation by Hiroshi Terada* Study abuot uncoupling agents in the respiratory chain …
(e.g. electron transport inhibitors and uncouplers, various quinonoid compounds, etc.) the mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species can increase severalfold (2, 3).
Inhibitors of electron transfer and oxidative phosphorylation have proved to be useful tools to investigate the mechanisms of energy-yielding reactions in living cells, and therefore, in the study d~scfibed here we have investigated the effect of these inhibitors in T. cruzi on (a) respiration, (b) the redox level of its cytochromes, (c) substrate oxida- tion reactions and (d) growth
A survey of the effect of inhibitors and uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation on chloroplast photophosphorylation led to the discovery of new inhibitors and uncouplers of this process. 2. n -Butyl-3,5-diiodo-4-hydroxybenzoate was found to inhibit both electron transport …
18/11/2008 · Answer to Question B-09 As described in a former post, the inhibitors of the Electron Transport Chain are substances that bind to some of the components of the ETC blocking its ability to change in a reversible form from an oxidized state to a reduced state.
• how various substrates, inhibitors, and uncouplers affect the rate of electron transport by monitoring changes in the rate of oxygen consumption; • how various electron donors affect P:O ratios.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) that accompanies the oxidation of NADH and other substrates by the mitochondrial electron transport chain
E. Describe the use of Respiratory Inhibitors in elucidating the sequence of electron transport. IV. Describe how the energy released by the Electron Transport Chain is used.
2 Prentice Hall c2002 Chapter 14 3 Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (1) Respiratory electron-transport chain (ETC) Series of enzyme complexes embedded in
Mechanism of Mitochondrial Uncouplers Inhibitors and
Inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation Biochemistry for
Inhibitors of electron transport chain Homework Help
Inhibitors of electron transfer and oxidative phosphorylation have proved to be useful tools to investigate the mechanisms of energy-yielding reactions in living cells, and therefore, in the study d~scfibed here we have investigated the effect of these inhibitors in T. cruzi on (a) respiration, (b) the redox level of its cytochromes, (c) substrate oxida- tion reactions and (d) growth
Evaluation of the electron transport chain inhibition and
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION AND THE ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
Electron Transport Chain Inhibitors and Uncouplers
uncouplers such as SF6847 can uncouple in the nanomolar range, whereas the less efficient uncouplers such as penta- chlorophenol and2,4-dinitrophenol are effective only in the
Electron Transport Chain an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Electron Transport Chain Inhibitors and Uncouplers
Electron Transport Chain II The ETS is composed of four large protein complexes in the inner mitochndrial membrane and are involved in transferring electrons from reduced carriers (coenzymes) to …
Electron Transport Chain The Biochemistry Questions Site
Bioenergetics Electron Transport Chain Cellular