Types of active transport pdf
Absorption in the Small Intestine (Human): Passive Transport © Diagram Visual Information Ltd. Most of the absorption carried out by the digestive
Active Transport Active Transport requires the cell to use energy, usually in the form of ATP. Active Transport creates a charge gradient in the cell membrane. For example in the mitochondrion, hydrogen ion pumps pump hydrogen ions into the intermembrane space of the organelle as part of making ATP.
356 physiol. chem. & physics 13 (1981) active solute transport across frog skin and epithelial cell systems according to the association-induction hypothesis
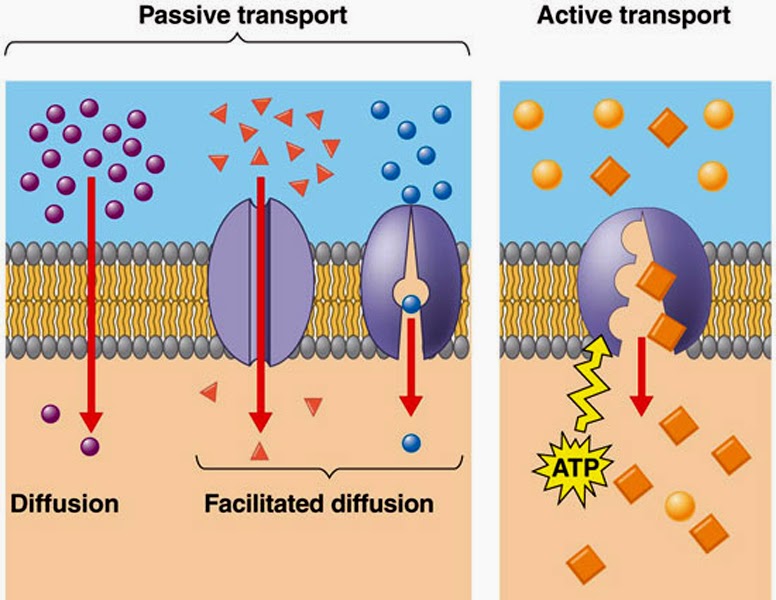
Passive transport is the movement of substances across the membrane without any input of energy from the cell. Osmosis and diffusion (the focus of the previous lesson) are two examples of passive transport.
The main types of movement across membranes are simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport and Bulk Transport (including exocytosis and endocytosis). It is sometimes described as types of transport through cell membranes. Knowledge about cell membranes is required for many courses in cell biology and biology in general.
In this lecture… •The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane –Components of the membrane •Active vs. passive transport •Diffusion and osmosis
Active transport is the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy; whereas, passive transport is a movement of biochemicals and other atomic or molecular substances across cell membranes.
In summary, we have learned that active transport is transport that requires chemical energy to move substances against a concentration gradient. There are three types of integral membrane
What is uniport symport antiport membrane transport

Summary of Membrane Transport Processes PhysiologyWeb
Active transport is the energy-demanding transfer of a substance across a cell membrane against its concentration gradient, i.e., from lower concentration to higher concentration. Special proteins within the cell membrane act as specific protein ‘carriers’.
2 Active transport The cell membrane also contains protein carrier molecules which can use energy to actively move molecules and ions through the membrane.
TRANSPORT ACROSS CELL MEMBRANE Two types of transport process occur across the membrane. 1. Non-mediated transport 2. Mediated transport Non-mediated transport occurs through the simple diffusion process and the driving force for
Osmosis, Diffusion and Cell Transport. Types of Transport There are 3 types of transport in cells: 1. Passive Transport: does not use the cell’s energy in bringing materials in & out of the cell 2. Active Transport: does use the cell’s energy in bringing materials in & out of the cell 3. Bulk Transport: involves the cell making membrane bound vesicles to bring materials in & out of the
I – Transport of Water and Nutrients in Plants – W.E. Riedell, T.E. Schumacher Phloem is composed of four cell types: parenchyma cells, fibers, sieve elements, and companion cells that are associated with sieve elements. Sieve elements, the basic transport cells of the phloem, are elongated cells similar to tracheids but are living at maturity (Figure 2). Sieve elements do not have a
Workshop Roundabouts Australia Australia March 2015 Typical capacity per type of roundabout single lane roundabout 25.000 veh/24h
Section Summary. Active transport methods require the direct use of ATP to fuel the transport. Large particles, such as macromolecules, parts of cells, or whole cells, can be engulfed by other cells in a process called phagocytosis.

Figure 1. Mechanisms of solute transport. Three distinct types of passive transport, as well as active transport, are illustrated. Passive transport is the movement of solute across a membrane down an electrochemical gradient (from the side of the membrane with a high concentration of solute to the side with a low concentration).
Transport systems may be passive or active. Passive transport proteins may be channels or facilitative transporters. Active transporters may be primary active transporters (pumps) or secondary active transporters (cotransporters and exchangers). See text for details.
The ‘Planning and Designing for Pedestrians: Guidelines’ is a unique collaboration of the Departments of Transport, Planning, Disability Services Commission, Main Roads WA, WA Local Government Association, Public Transport Authority, The …
In a recent review of the transport of salts and water across multicellular secretory tissues in animals (Keynes, 1969), a summary was given of the various types of active transport of ions necessary to explain the experimental observations in a very wide range of tissues, and five basic types …
Facilitated diffusion and active transport are two ways of moving materials across the cell membrane. These two types of transport have many similarities as well as differences.
Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses energy to transport molecules across a membrane. Example:Sodium-potassium pump, which helps …
Active transport is important for cellular function because it moves important items, such as calcium and glucose, into and out of cells. Proteins sit on the cell membrane, with one part inside and one part outside the membrane.
Difference Between Passive and Active Transport The main difference is the fact that passive transport does not require any energy, whereas active transport requires energy for movement. Passive transport is basically along the concentration gradient, and is mostly dependent on the permeability of the cell membrane structure.
Passive and Active Transport Pearson
Moreton Bay Regional Council Active Transport Strategy 2012 – 2031 4 Active transport facilities Moreton Bay Regional Council plans, delivers and maintains a variety of active transport infrastructure and facilities. These facilities support a variety of active transport options. The scope of this strategy includes both Council and State -managed facilities. Council-provided active
Passive and Active Transport 1. Thermodynamics of transport 2. Passive-mediated transport 3. Active transport neuron, membrane potential, ion transport
Public transport can have various types of benefits and costs, many of which tend to be overlooked or undervalued in conventional transportation economic evaluation. Conventional transport economic evaluation tends to overlook and undervalue many transit
Active transport of solutes against their electrochemical gradient is essential to maintain the intracellular ionic composition of cells and import solutes that …
• Two types of assisted transport • Carrier mediated transport • May be passive or active • Small molecules • Vesicular transport • Always active • Very large molecules, particles Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Assisted 10 Background Material Assisted Membrane Transport • Carrier mediated transport • Carriers are proteins that span the membrane • They
facilitated diffusion osmosis passive transport active transport For each scenario, answer the questions and draw an ARROW to illustrate the movement of molecules. 14.
affinities, via a secondary active transport mechanism. The of the kidneys. The first of this type of glucose transport protein to be cloned was the high-affinity transporter from rabbit intestine, SGLT1 (Hediger et al. 1987). The human analogue soon followed by homology cloning (Hediger et al. 1989). Amino acid comparisons of the human SGLT range from 57–71% sequence identity (GAP
1 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Passive and Active Transport Background: Substances are routinely transported (received and delivered) across the cell plasma membranes. – transport canada issued candidate document number Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient, that is, if the concentration of the substance inside the cell must be greater than its concentration in the extracellular fluid, the cell must use
Types of active transport Endocytosis- large particles move into the cell. Receptor mediated endocytosis- moves specific Types of passive transport Facilitated diffusion-moves high to low with protein. Diffusion- moves high to low with no protein. Hypotonic- water moves inside the cell, and cell
ic type of ion to pass from one side of the cell membrane to the other. This passive This passive transport, which requires no expenditure of energy, is an example of facilitated dif-
Primary active transport utilizes energy in form of ATP to transport molecules across a membrane against their concentration gradient. Therefore, all groups of ATP-powered pumps contain one or more binding sites for ATP, which are always present on the cytosolic face of the membrane.
Active and passive transport are biological processes that move oxygen, water and nutrients into cells and remove waste products. Active transport requires chemical energy because it is the movement of biochemicals from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration.
Cycling or walking to and from work linked to substantial health benefits – Medical Xpress Why driverless vehicles should not be given unchecked access to our cities – Phys.org Global health disruptors: Climate change – blogs.bmj.com
68 Diffusion and Transport Across Cell Membranes SUPPLEMENTAL READING Boron and Boulpaep, Medical Physiology, Saunders, 2003. pp. 56-71. (This section is detailed, but contains useful descriptions of nearly every type of
Active and passive transport processes are two ways molecules and other materials move in and out of cells and cross intracellular membranes. Active transport is the movement of molecules or ions against a concentration gradient (from an area of lower to higher concentration), which does not ordinarily occur, so enzymes and energy are required.
There are two types of transport: active transport, and passive transport. Passive transport is easiest for the cells because they don’t need to use any energy to make it happen. Diffusion is the simplest and most common form of passive transport. During the diffusion process, tiny particles of the materials that need to be delivered to the cells are spread through either a gas, like oxygen
QUIZ: DIFFUSION. 1. Which of the following is NOT a type of passive transport? diffusion osmosis endocytosis facilitated diffusion . 2. Chamber A contains 40% …
There are four different types of passive transport: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, filtration and osmosis. Diffusion is the movement of substances from an area of high concentration to …
Passive Transport – Taking the Easy Road While active transport requires energy and work, passive transport does not. There are several different types of this easy movement of molecules.
Active transport describes the process whereby the transport of specific substances is coupled to ATP hydrolysis. Because the energy for transport is derived from ATP hydrolysis , these transporters effectively move substances in one direction, regardless of the concentration gradient.
Active and Passive Transport: Red Rover Send Particles Over activity — Types of Transport Activity Sheet Types of Transport Activity Sheet At the conclusion of this activity, students should be able to:
31/08/2012 · Mrs. Inabinet describes the two types of active transport, 1) endocytosis and 2) exocytosis.
Active Transport Video · BrainPOP is a website with great video clips on many science topics, unfortunately you have to pay for an account to access any of the information, and the videos/documents cannot be downloaded to your computer.
Why Is Active Transport Important? Reference.com
Transport across a cell membrane is a tightly regulated process, because cell function is highly dependent on maintain strict concentrations of various molecules. When a molecule moves down its concentration gradient is it participating in passive transport; moving up the concentration gradient requires energy making it active transport.
passive transport examples, explain why active transport requires energy input by the cell. 31.Complete the table below to show the difference between active and passive transport. 32.Formulate a definition for active transport.
active transport is especially important in maintaining ion concentration in cells and between cells. Carrier proteins first binds with a particle of the substance to be transported. Carrier protein must be a similar shape that fits the molecule or ion that it is binding to.
The three major classes of membrane transport proteins are depicted in Figure 15-3a. All are integral transmembrane proteins and exhibit a high degree of specificity for the substance transported. The rate of transport by the three types differs considerably owing to differences in their mechanism of action. Figure 15-3Schematic diagrams illustrating action of membrane transport
Active and passive transport are the two main biological process which plays an important role in supplying nutrients, water, oxygen and other essential molecules to cells and also by …
Passive and Active Transport Biol230W Fall09 – Confluence

Difference Between Active Transport and Passive Transport
Active Transport is the term used to describe the processes of moving materials through the cell membrane that requires the use of energy. There are three main types of Active Transport: The Sodium-Potassium pump, Exocytosis, and Endocytosis.
Active Transport Active transport is similar to the preceding two mechanism in that specific binding of the transported substance occurs. However, here ATP is …
Passive transport is a movement of ions and other atomic or molecular substances across cell membranes without need of energy input. Unlike active transport, it does not require an input of cellular energy because it is instead driven by the tendency of the system to grow in entropy.
Learn more about what the membrane’s made of and how different types of molecules move across it. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more.
Glucose transporters (GLUT and SGLT) expanded families of

Active Transport Strategy 2012-2031 Moreton Bay Regional
Active transport requires energy inside the kind of ATM whereas passive transport would not. In energetic transport molecules switch in opposition to the main focus gradient nevertheless in passive transport, molecules switch from extreme to low focus.. Types of energetic transport are endocytosis, exocytosis. Types of passive transport embrace, osmosis, diffusion. Anything soluble is
This quiz and corresponding worksheet will help you gauge your knowledge of passive and active transport in the cells. Questions will assess your understanding how a substance can move from an
value of the health benefits of active transport modes, in order to include it in cost-benefit analyses for transport and other government sectors. In transport cost-benefit analysis, the Land Transport NZ Economic evaluation manual (EEM2) currently
Variety of worksheets to both introduce active transport and compare with diffusion and osmosis
There are two types of active transport: primary active transport that uses ATP, and secondary active transport that uses an electrochemical gradient. An example of active transport in human physiology is the uptake of glucose in the intestines .
Passive transport is the cellular process of moving molecules and other substances across membranes. Passive transport differs from active transport in that it does not involve any chemical energy. Rather, passive transport relies on the innate permeability of the cell membrane and its component proteins and lipids.
Uniport (a single substance, moves in a single direction) Symport (two substances, moves in the same direction) Antiport (two substances, moves in opposite directions)
• Means of Transport • Transport in India Chapter-1 . 1.1 INTRODUCTION From the beginning of history, human sensitivity has revealed an urge for mobility leading to a measure of Society’s progress. The history of this mobility or transport is the history of civilization. For any country to develop with right momentum modern and efficient Transport as a basic infrastructure is a must. It
Quiz & Worksheet Passive & Active Transport in Cells


PDF Victoria Transport Institute – Main Page
Active Transport Moves solute Against Their
– Workshop Roundabouts Australia transport.wa.gov.au
Active Transport YouTube


Membranes and transport Biology Science Khan Academy
Primary and Secondary Active Transport WikiLectures
Active and Passive Transport Red Rover Send Particles
Active and Passive Transport Difference and Comparison
This quiz and corresponding worksheet will help you gauge your knowledge of passive and active transport in the cells. Questions will assess your understanding how a substance can move from an
Passive and Active Transport 1. Thermodynamics of transport 2. Passive-mediated transport 3. Active transport neuron, membrane potential, ion transport
affinities, via a secondary active transport mechanism. The of the kidneys. The first of this type of glucose transport protein to be cloned was the high-affinity transporter from rabbit intestine, SGLT1 (Hediger et al. 1987). The human analogue soon followed by homology cloning (Hediger et al. 1989). Amino acid comparisons of the human SGLT range from 57–71% sequence identity (GAP
• Means of Transport • Transport in India Chapter-1 . 1.1 INTRODUCTION From the beginning of history, human sensitivity has revealed an urge for mobility leading to a measure of Society’s progress. The history of this mobility or transport is the history of civilization. For any country to develop with right momentum modern and efficient Transport as a basic infrastructure is a must. It
Absorption in the Small Intestine (Human): Passive Transport © Diagram Visual Information Ltd. Most of the absorption carried out by the digestive
Passive transport is the cellular process of moving molecules and other substances across membranes. Passive transport differs from active transport in that it does not involve any chemical energy. Rather, passive transport relies on the innate permeability of the cell membrane and its component proteins and lipids.
Workshop Roundabouts Australia Australia March 2015 Typical capacity per type of roundabout single lane roundabout 25.000 veh/24h
Passive transport is a movement of ions and other atomic or molecular substances across cell membranes without need of energy input. Unlike active transport, it does not require an input of cellular energy because it is instead driven by the tendency of the system to grow in entropy.
Active Transport Active transport is similar to the preceding two mechanism in that specific binding of the transported substance occurs. However, here ATP is …
Passive and Active Transport unifr.ch
Passive Transport – College-Cram Biology
The three major classes of membrane transport proteins are depicted in Figure 15-3a. All are integral transmembrane proteins and exhibit a high degree of specificity for the substance transported. The rate of transport by the three types differs considerably owing to differences in their mechanism of action. Figure 15-3Schematic diagrams illustrating action of membrane transport
Workshop Roundabouts Australia Australia March 2015 Typical capacity per type of roundabout single lane roundabout 25.000 veh/24h
facilitated diffusion osmosis passive transport active transport For each scenario, answer the questions and draw an ARROW to illustrate the movement of molecules. 14.
The ‘Planning and Designing for Pedestrians: Guidelines’ is a unique collaboration of the Departments of Transport, Planning, Disability Services Commission, Main Roads WA, WA Local Government Association, Public Transport Authority, The …
Absorption in the Small Intestine (Human): Passive Transport © Diagram Visual Information Ltd. Most of the absorption carried out by the digestive
In summary, we have learned that active transport is transport that requires chemical energy to move substances against a concentration gradient. There are three types of integral membrane
2 Active transport The cell membrane also contains protein carrier molecules which can use energy to actively move molecules and ions through the membrane.
The three major classes of membrane transport proteins are depicted in Figure 15-3a. All are integral transmembrane proteins and exhibit a high degree of specificity for the substance transported. The rate of transport by the three types differs considerably owing to differences in their mechanism of action. Figure 15-3Schematic diagrams illustrating action of membrane transport
Active and Passive Transport Difference and Comparison
Active transport Wikipedia
Membrane Transport Unassisted Membrane Transport UCY